Grokking Interview Topics
- Sliding Window
- Two Pointers
- Fast & Slow Pointers
- Merge Intervals
- Cyclic Sort
- In-place Reversal of a LinkedList
- Tree Breadth-First Search
- Tree Depth First Search
- Two Heaps
- Subsets
- Modified Binary Search
- Bitwise XOR
- Top ‘K’ Elements
- K-way Merge
- 0/1 Knapsack
- Unbounded Knapsack
- Fibonacci Numbers
- Palindromic Subsequence
- Longest Common Substring
- Topological Sort
- Trie Traversal
- Number of Island
- Trial & Error
- Union Find
- Unique Paths
- Monotonic Stack
Following is a small intro of each of these patterns with sample problems:
1. Sliding Window
Usage: This algorithmic technique is used when we need to handle the input data in specific window size.

Sliding Window Pattern
Sample Problems:
2. Two Pointers
Usage: In this technique, we use two pointers to iterate the input data. Generally, both pointers move in the opposite direction at a constant interval.

Two Pointers Pattern
Sample Problems:
3. Fast & Slow Pointers
Usage: Also known as Hare & Tortoise algorithm. In this technique, we use two pointers that traverse the input data at a different speed.
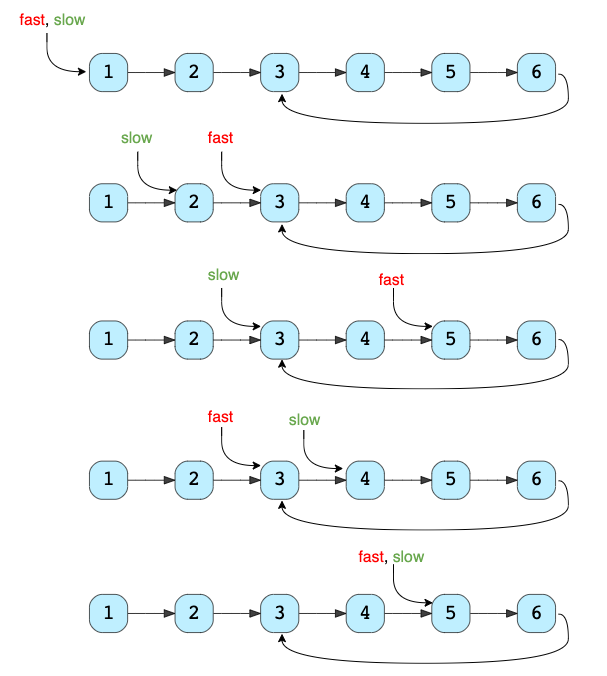
Fast & Slow Pointers Pattern
Sample Problems:
4. Merge Intervals
Usage: This technique is used to deal with overlapping intervals. Given two intervals (‘a’ and ‘b’), there will be six different ways the two intervals can relate to each other:
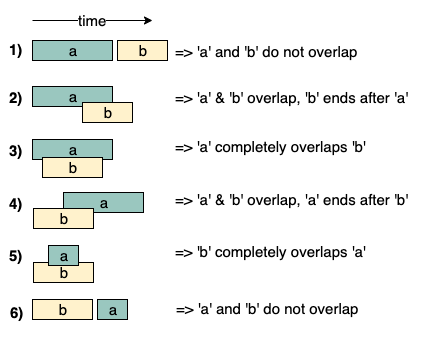
Intervals Overlapping
Sample Problems:
5. Cyclic Sort
Usage: Use this technique to solve array problems where the input data lies within a fixed range.
Sample Problems:
6. In-place Reversal of a LinkedList
Usage: This technique describes an efficient way to reverse the links between a set of nodes of a LinkedList. Often, the constraint is that we need to do this in-place, i.e., using the existing node objects and without using extra memory.



Sample Problems:
7. Tree Breadth-First Search
Usage: As the name suggests, this technique is used to solve problems involving traversing trees in a breadth-first search manner.
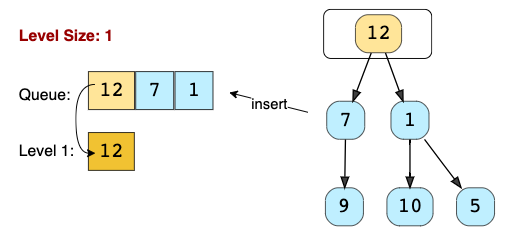
Binary Tree Breadth-First Search
Sample Problems:
8. Tree Depth First Search
Usage: As the name suggests, this technique is used to solve problems involving traversing trees in depth-first search manner.
Sample Problems:
9. Two Heaps
Usage: In many problems, where we are given a set of elements such that we can divide them into two parts. We are interested in knowing the smallest element in one part and the biggest element in the other part. As the name suggests, this technique uses a Min-Heap to find the smallest element and a Max-Heap to find the biggest element.
Sample Problems:
10. Subsets
Usage: Use this technique when the problem asks to deal with permutations or combinations of a set of elements.
Sample Problems:
11. Modified Binary Search
Usage: Use this technique to search a sorted set of elements efficiently.
Sample Problems:
12. Bitwise XOR
Usage: This technique uses the XOR operator to manipulate bits to solve problems.
Sample Problems:
13. Top ‘K’ Elements
Usage: This technique is used to find top/smallest/frequently occurring ‘K’ elements in a set.
Sample Problems:
14. K-way Merge
Usage: This technique helps us solve problems that involve a list of sorted arrays.
Sample Problems:
15. 0/1 Knapsack
Usage: This technique is used to solve optimization problems. Use this technique to select elements that give maximum profit from a given set with a limitation on capacity and that each element can only be picked once.
Sample Problems:
16. Unbounded Knapsack
Usage: Use this technique to select elements that give maximum profit from a given set with a limitation on capacity and that each element can be picked multiple times.
Sample Problems:
17. Fibonacci Numbers
Usage: Use this technique to solve problems that follow the Fibonacci numbers sequence, i.e., every subsequent number is calculated from the last few numbers.
Sample Problems:
18. Palindromic Subsequence
Usage: This technique is used to solve optimization problems related to palindromic sequences or strings.
Sample Problems:
19. Longest Common Substring
Usage: Use this technique to find the optimal part of a string/sequence or set of strings/sequences.
Sample Problems:
20. Topological Sort
Usage: Use this technique to find a linear ordering of elements that have dependencies on each other.
Sample Problems:
21. Trie Traversal
Usage: Use this technique that involves creating or traversing of Trie data structure.
Sample Problems:
- Longest Word in Dictionary
- Palindrome Pairs
22. Number of Island
Usage: Use this technique to traverse a two-dimensional array and find a set of connected elements.
Sample Problems:
- Number of Distinct Islands
- Maximum Area of Island
23. Trial & Error
Usage: Use this technique to traverse an array to find a required optimal element. The traversal process runs in a trial & error manner.
Sample Problems:
- Find Kth Smallest Pair Distance
- Minimize Max Distance to Gas Station
24. Union Find
Usage: Use this technique to solve problems that require maintaining a given set of elements partitioned into multiple non-overlapping subsets.
Sample Problems:
- Number of Provinces
- Bipartite Graph
25. Unique Paths
Usage: Use this technique to find different/optimal ways to traverse a multi-dimensional array.
Sample Problems:
- Find Unique Paths
- Dungeon Game
26. Monotonic Stack
Description: This pattern involves using a stack to maintain a monotonic (either entirely non-increasing or non-decreasing) order of elements.
Usage: It's often used for solving problems where you need to find the next greater or smaller elements.
Problems: 'Next Greater Element', 'Next Smaller Element', 'Largest Rectangle in Histogram'.